
The future of education is being rewritten. Social emotional learning (SEL) and virtual reality (VR), once seen as extras, are quickly becoming essentials. Together, they’re not just transforming classrooms; they’re reshaping how kids are learning life skills like resilience, empathy, and teamwork.
Play has always been the foundation of growth. Now, the world is finally catching up— parents, teachers, and institutions alike are realizing that fun is where real skills take root. And as SEL and VR rise in parallel, one truth is becoming clear: when these forces converge, they open the door to a new kind of education— social, immersive, and built on the skills kids need most for life.
In this article, the first of a three-part series, we’ll explore why SEL and VR are growing so quickly, where the gaps remain, and why their convergence is creating a rare opportunity. In Part 2, we’ll look at how parents are leading the way in shaping this future. In Part 3, we’ll unpack the design principles— story, loops, and interaction— that make SEL in VR work.
The Market for Learning Life Skills Is Growing
The numbers tell a compelling story.
- Canada’s SEL Market: In Canada, the SEL market generated USD 178.1 million in 2023 and is projected to climb to USD 849.7 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of ~25% (Grand View Research, 2023).
- Global SEL Market: Worldwide, SEL is projected to expand from USD 3.6 billion in 2023 to USD 10.3 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 23.6% (MarketsandMarkets, 2023).
- Asia-Pacific Momentum: The Asia-Pacific SEL market is forecast to grow even faster, from USD 707 million in 2023 to USD 2.2 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 25.4% (MarketsandMarkets, 2023).
- VR in Education: Globally, VR in education is expected to rise from USD 17.18 billion in 2024 to USD 65.55 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 18.2% (Fortune Business Insights, 2024).
- Global Long-Term Forecast: Other reports predict VR in education will reach USD 188.7 billion by 2035, growing at ~25% annually (Market Research Future, 2024).
- Headset Adoption: Between 2024 and 2028, more than 5.5 million new VR headsets are expected to be added worldwide, representing ~25% growth (VirtualSpeech, 2024).
While the data tracks SEL and VR separately, their parallel growth points to a shared direction: countries are not only prioritizing emotional skills and mental health, but also experimenting with immersive technologies. This creates fertile ground for tools that combine both into new approaches for learning life skills.
Why Learning Life Skills in VR Matters Now
Today’s kids are not just visiting the internet— they are born into it. Screens are their playgrounds.
Yet while play remains central to learning, much of that play happens in unguided digital spaces. Without direction, those spaces can feel chaotic, unkind, or even unsafe. Parents and educators alike see the impact: kids are glued to screens, but not always learning life skills that serve them in life.
At the same time, schools remain focused on grades. However, grades alone don’t predict long-term success. In fact, 85% of career achievement comes from soft skills like communication, teamwork, and resilience (WiseWorld AI, 2024).
This is why SEL matters now more than ever. VR, when paired with SEL, offers one of the most promising solutions. It transforms screen time into intentional, active life skill learning experiences.
Institutional Support Around the World
Support for SEL and VR is not just coming from families— it is also growing within institutions. Across K-12 schools, universities, and training programs, both social emotional learning and immersive technology are being adopted at scale.
- SEL in Teacher Training and Schools:
Saint Elizabeth University (SEU) has launched a SEL & Character Development Initiative that embeds SEL into teacher education and counseling programs, preparing future educators to foster positive classroom climates and help students practice resilience and empathy. Similarly, school districts across North America are adopting universal SEL programs, guided by frameworks like CASEL, to integrate social emotional skills into daily instruction and school culture. - Higher Education SEL Programs:
Universities are also formalizing SEL education. The University of British Columbia, for example, offers a Master of Education in Social & Emotional Learning, equipping educators with advanced tools to bring SEL practices into their schools. These initiatives demonstrate that SEL is no longer just a classroom trend— it’s becoming an institutional priority. - VR for Experiential Learning:
Alongside SEL programs, VR is transforming how institutions deliver experiential education. At Harvard, faculty like Nicole Mills have integrated VR into language courses, allowing students to immerse themselves in Parisian life and reflect critically on cultural stereotypes (Harvard VPAL, 2024). At UNSW in Australia, researchers have built low-cost VR field trips that let students explore Mars (OpenGov, 2024). And at St. John’s University, health sciences students train with virtual reality technology (St. John’s University, 2024).
Together, these examples show that SEL and VR are both being recognized by institutions as essential for future learning. When combined, they hold the potential to create immersive, emotionally meaningful environments where students can practice the learning of life skills they’ll need for life.
Where the Gaps Are
Despite strong growth, most current tools fall short.
- Traditional SEL programs often rely on static worksheets, videos, or role-playing activities that fail to engage digital-native learners. As a result, many kids miss out on opportunities for learning life skills in ways that feel relevant.
- Many VR tools, while powerful, are focused on STEM, single-player experiences, or corporate simulations. They rarely emphasize SEL skills like resilience, empathy, and teamwork.
This creates a clear gap in the market: very few solutions combine immersive VR with multiplayer SEL experiences.
Competitors in the Space
Here are some of the education and immersive tools shaping the space today:
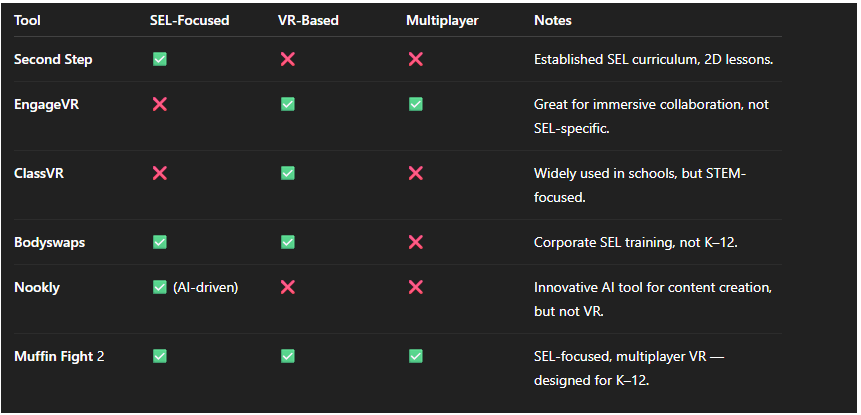
What stands out is not just the growth, but the gap. Each of these tools plays an important role in expanding what’s possible:
- Second Step has established itself as one of the most widely used SEL curricula, helping schools adopt consistent language and frameworks for social emotional growth.
- Engage shows the power of virtual collaboration, making immersive classrooms possible at scale.
- ClassVR has opened the door for many schools to try VR in STEM subjects, proving adoption pathways.
- Bodyswaps demonstrates how SEL can be applied in corporate and professional training through simulation.
- Nookly highlights the potential of AI to support creativity and personalized learning.
Yet few of these tools combine SEL + VR + multiplayer— the sweet spot where kids can actively practice resilience, empathy, and teamwork in playful, immersive spaces. This is the missing link in life skill learning through digital play.
That’s the niche Muffin Fight 2 fills— not by replacing what others do, but by extending the ecosystem with a K-12-focused solution that puts social-emotional growth at the center of active, digital play.
The Opportunity Ahead
Bringing SEL and VR together in education isn’t just a fad— it’s a real shift. It is a chance to design digital playgrounds where kids can practice the skills that research proves they need most:
- Resilience through frustration and recovery.
- Empathy through teamwork and cooperation.
- Confidence through risk-taking in safe, playful spaces.
As the demand for social emotional skills expands and VR adoption accelerates in schools, one thing is clear: the future of learning will be social, immersive, and built on real-world skills. In other words, VR is becoming one of the most powerful pathways for learning life skills in the digital age.
The question is no longer if SEL and VR will shape education. The real question is: who will shape these new playgrounds first?
In many ways, the answer is already here: parents. Families are making choices about screen time every day, and they are setting the tone for what comes next.
In our next article, we’ll look at why parents, not schools, are leading the way in shaping how kids experience VR and social-emotional learning.
Further Reading
VirtualSpeech. (2024). VR statistics for training and education. Retrieved from https://virtualspeech.com/blog/vr-stats-training-education
MarketsandMarkets. (2023). Social-emotional learning market – Global forecast to 2028. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/social-emotional-learning-market-245017024.html?utm_source=chatgpt.com
WiseWorld AI. (2024). Soft skills for career success. Retrieved from https://www.wiseworld.ai/blog/soft-skills-for-career-success
Grand View Research. (n.d.). Canada social and emotional learning (SEL) market size & outlook, 2030. Retrieved from https://www.grandviewresearch.com/horizon/outlook/social-and-emotional-learning-sel-market/canada Grand View Research
Fortune Business Insights. (2024, July 10). Virtual reality in education market to grow at a CAGR of 18.2% over 2024 to 2032. Retrieved from https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/press-release/virtual-reality-in-education-market-9400 Fortune Business Insights
Market Research Future. (n.d.). Virtual reality education market size, future scope to 2034. Retrieved from https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/virtual-reality-education-market-24045

